42 nematocysts discharge when
A sea anemone's environment affects discharge of its isolated nematocysts Undischarged acontial nematocysts were isolated by extrusion into 1 M sodium citrate and were then treated with 5 mM EGTA to initiate discharge. Nematocysts isolated from anemones maintained under three different feeding schedules showed significantly different responses to the test solution. Formation and discharge of nematocysts is controlled by a proton ... Nematocysts of Hydra do not discharge when not treated with distilled water, but when transferred to saturated NaCl solution. About ten H. vulgaris were placed on the top of a FET in about 15 μl culture medium. Following the application of 10-20 μl saturated NaCl solution, the pH dropped to minimally 6.0 (Table 1 ).
Activity: Nematocysts | manoa.hawaii.edu/ExploringOurFluidEarth Observe how the nematocysts react to the hair root. Test the response of the nematocysts to saliva. Place several drops of saliva on one end of a second glass slide. Get a fresh piece of tentacle and place it close to the saliva. Move the saliva onto the tentacle with a toothpick while your partner watches the tentacle through the microscope.

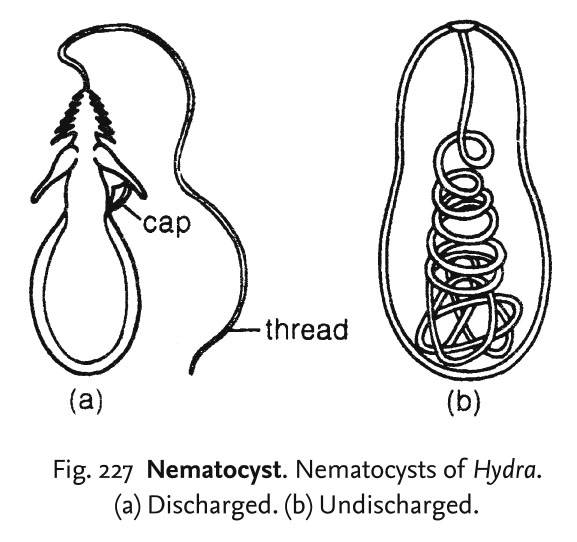
Nematocysts discharge when
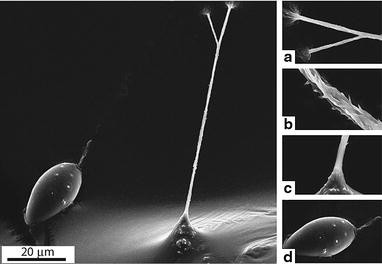
Nanosecond-scale kinetics of nematocyst discharge - Current Biology The rapid discharge of stinging cells (nematocytes) in jellyfish, hydra, and other cnidarians is one of the fastest movements in the animal kingdom. After the triggering of exocytosis, a miniature cellular weapon, the nematocyst, is released and stylets punch a hole into the prey's integument. This step is so fast that conventional high-speed micro-cinematography fails to resolve its kinetics [1]. Cnidaria Toxicity - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Nematocysts are hollow, barbed tubes that inject venom into the victim's skin at a force of two to five pounds per square inch (13-34 kPa). The nematocysts are located along the jellyfish's tentacles and discharge using a "spring mechanism" upon contact with the prey.[1] The stinging mechanism can still function even if the organism is dead. The Cell Biology of Nematocysts - ScienceDirect The ability of epidermal stenotele nematocysts to discharge suggest that this hydra organelle preserved its physiological properties in the new host. Research article. Nematocyst types and venom effects of Aurelia aurita and Velella velella from the Mediterranean Sea. Toxicon, Volume 175, 2020, pp. 57-63.
Nematocysts discharge when. Cnidarian - Life cycles, ecology & uses | Britannica The nematocysts of cnidarians restrict potential predators to a limited array of specialists. Nematocysts also allow cnidarians to prey on a variety of would-be competitors for space and food. Most species that are capable of monopolizing space reproduce predominantly asexually. Nematocyst Stingers Accelerate Fast — Biological Strategy - AskNature When the sensory portion of the cell (cnidocil) is mechanically disturbed (e.g., by contact with prey) it causes a rapid increase in the calcium ion concentration in the cell. This causes molecular rearrangement of the opeculum allowing the release of the nematocyst's stored pressure towards the outside of the organism. Nematocyst Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary What causes nematocysts to discharge? Electrostatic repulsion, osmotic pressure generation, and conformational change at the inner tubule's surface are the three driving factors involved in nematocyst discharge, all of which come from a loss of protons. However, the influence of these several factors may change depending on the type of cyst. Excitation of Nematocysts | Nature On the other hand, cotton wool soaked in food solution causes extensive discharge of nematocysts into the mass on contact. This is true even though the food solution employed is far below the ...
Nematocysts Firing - YouTube Microscopic video footage of jellyfish nematocysts firing. The video was created by the TASRU (Tropical Australian Stinger Research Unit) of James Cook Unive... How Do Jellyfish Sting? - Ocean Conservancy Apr 26, 2021 · Nematocysts are one technique used by members of the phylum Cnidaria that really packs a punch. First things first: what are cnidarians? Members of the phylum Cnidaria are invertebrates, meaning they don’t have a backbone. Cnidarians include corals, jellyfish, anemones and hydroids, and there are more than 11,000 species found all over the world. What is the main function of nematocysts? - KnowledgeBurrow.com The nematocyst is used to capture prey and may also be used for defense purposes. When it is triggered to discharge, the extremely high osmotic pressure within the nematocyst (140 atmospheres) causes water to rush into the capsule, increasing the hydrostatic pressure and expelling the thread with great force. When do Nematocysts discharge? - Answers Nematocyst discharge is triggered by an immediate approach or a foreign stimulus. When the cell is discharged, a brand new nematocyst is created as the system in each cell can only be activated...
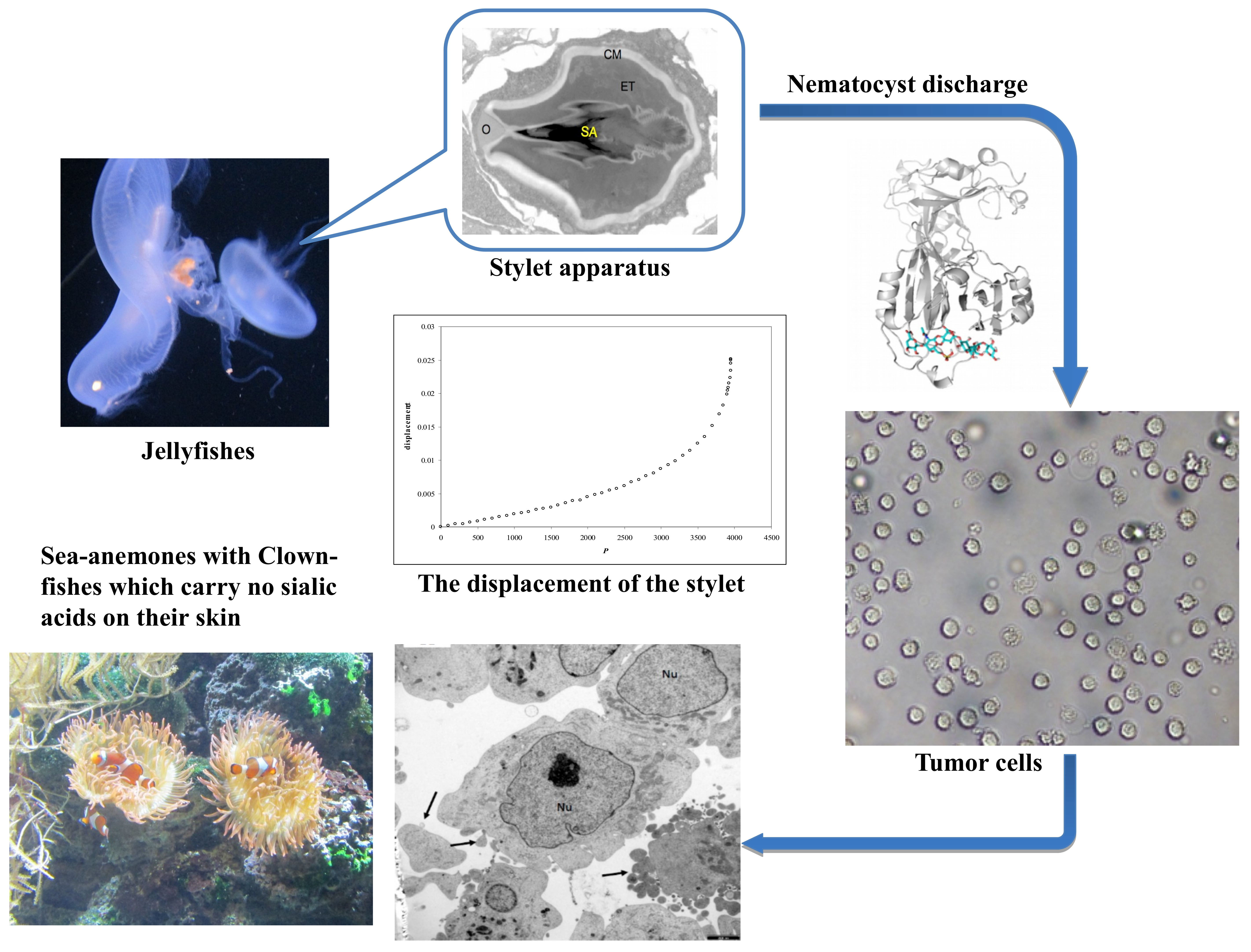
Nematocyst - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Nematocysts may also be deactivated by topical application of alcohol, weak acid solutions and possible weak bases. Although recommendations vary with region, there is good clinical experience inactivating the nematocysts of most species (Chironex, Chrysaora, and Cyanea) using household vinegar (5% acetic acid) or isopropyl alcohol (50–70%). The value of ethyl alcohol, which is often present on the beaches where these stings occur, and often contributes to the misadventure in the first ... The architecture and operating mechanism of a cnidarian stinging ... The nematocysts discharge in vivo when the medium becomes acidic. Primary polyps were immobilized in glass bottom dishes by sandwiching between a glass slide and the bottom of a glass bottom dish ... Stages Of Nematocyst Discharge - Lara Sheppard Discharge mechanism of a nematocyst. Stages of (stenotele) nematocyst discharge: Nematocysts are the means by which coelenterates capture prey and defend against predation. Heavy metals • nematocysts • discharge • crude venom • jellyfish • pelagia. The cnidocyst capsule stores a large concentration of calcium ions, which . What Causes Nematocysts To Discharge? - WWFAQs In summary we suggest that three driving forces are involved in the discharge of nematocysts, all resulting from a loss of protons: electrostatic repulsion, generation of osmotic pressure, and conformational change at the inner tubule's surface. What triggers a nematocyst to activate? Do the nematocysts discharge? Do nematocysts eject a barb?
Effects of Ions on Nematocysts Isolated From Acontia of the Sea Anemone Average percentages of discharged nematocysts 1 h after the application of 5 mmol 1 -1 EGTA or 5 mmol 1 -1 EGTA in 1moll -1 sucrose are shown. Although EGTA induced the discharge of isolated nematocysts to varying degrees, sucrose partially or almost completely blocked the EGTA-induced discharge. Bars represent standard errors.
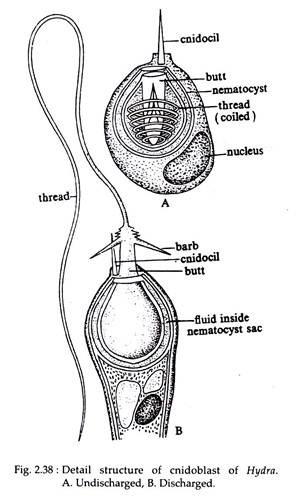
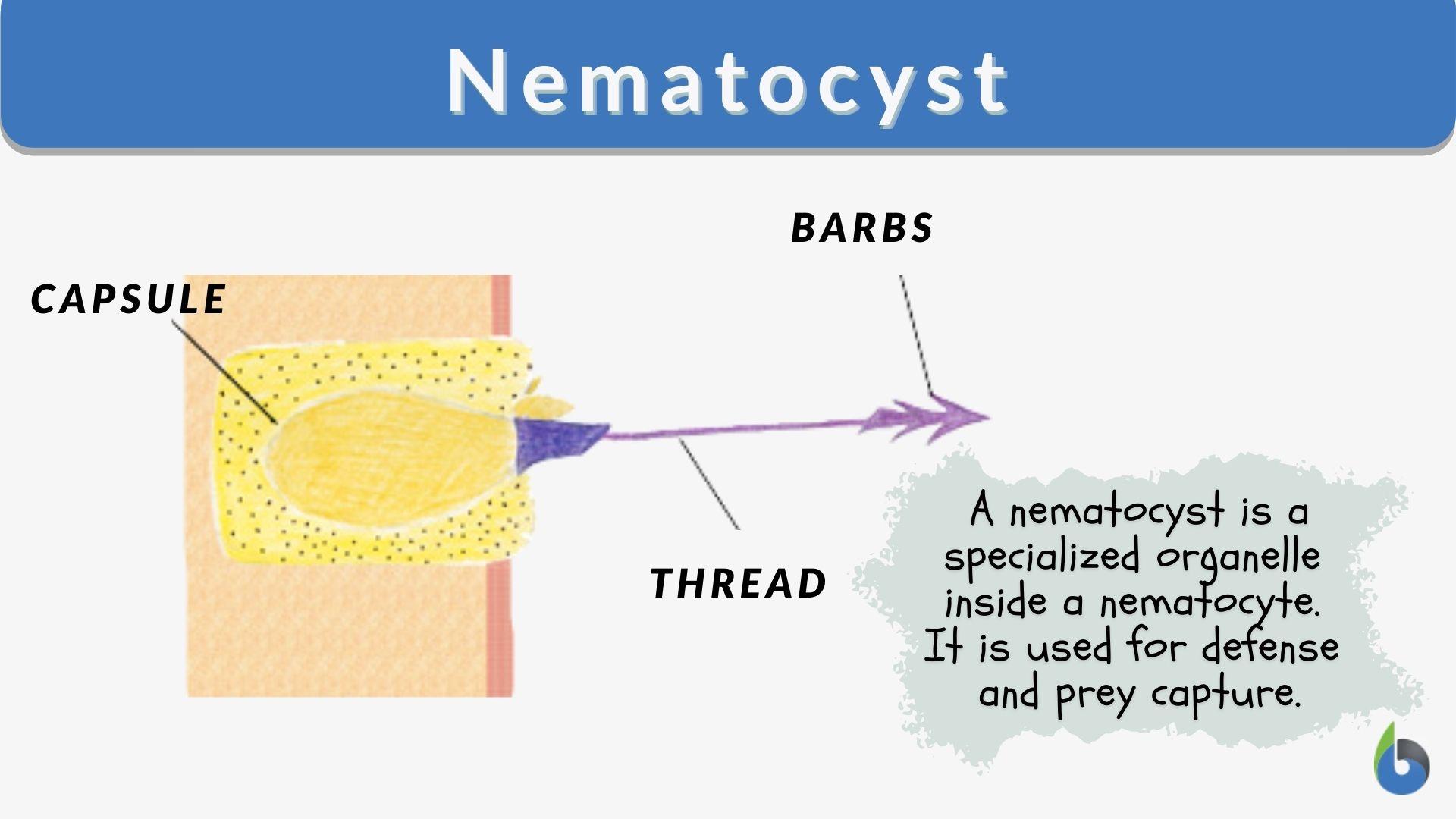
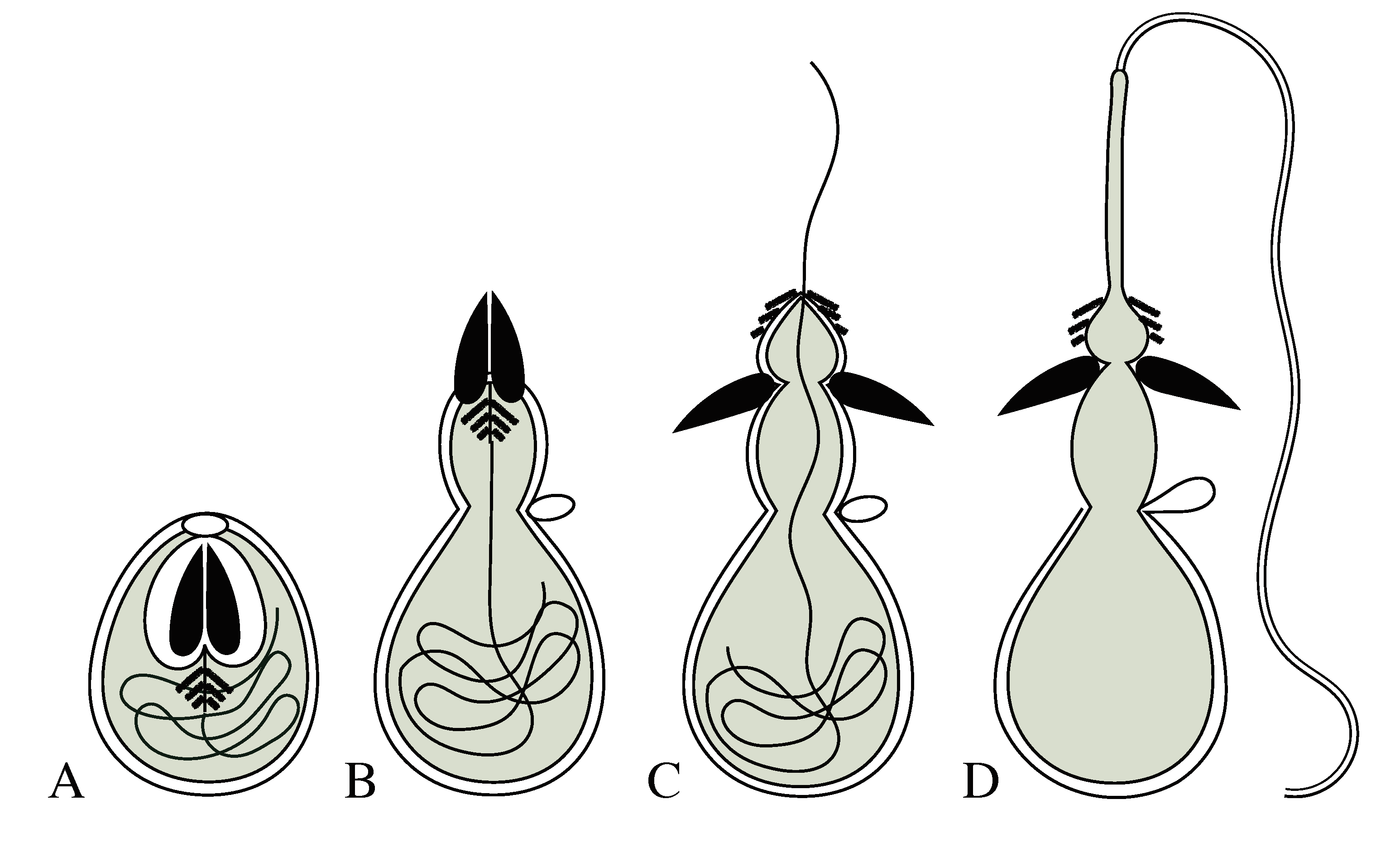
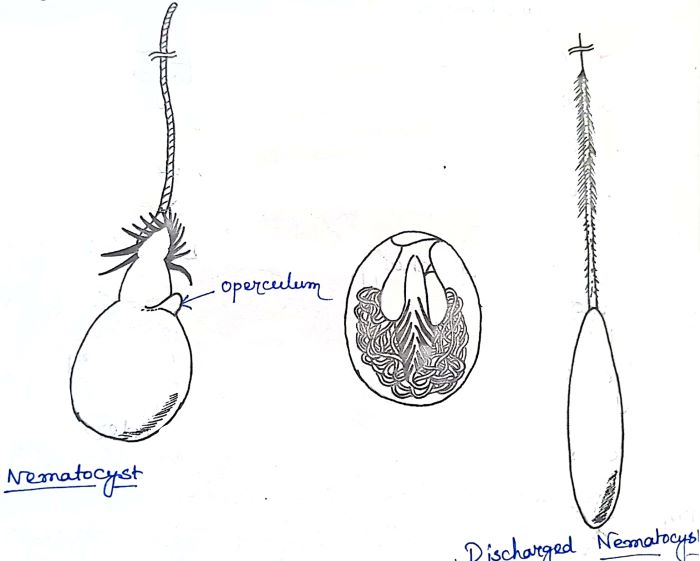
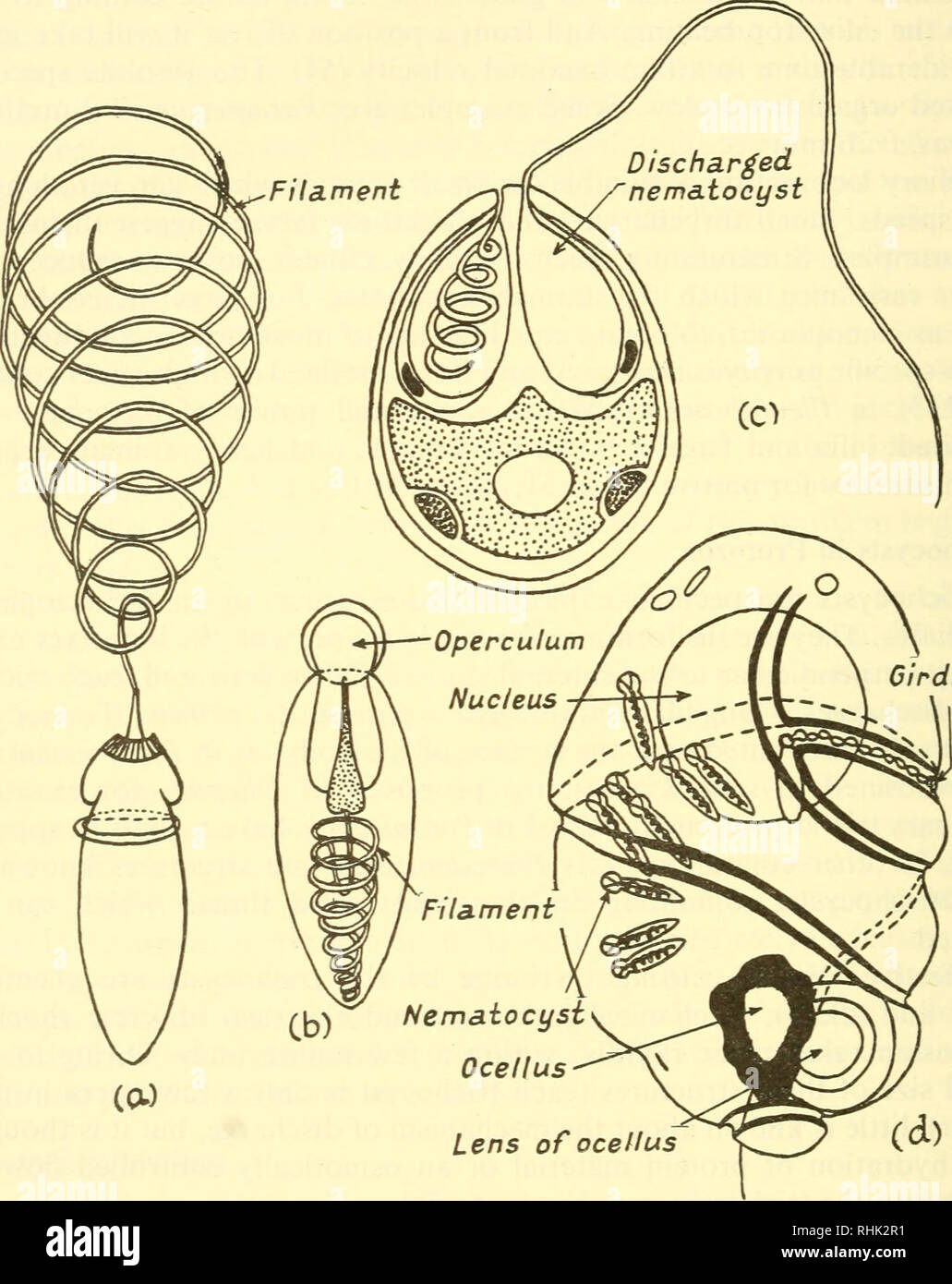
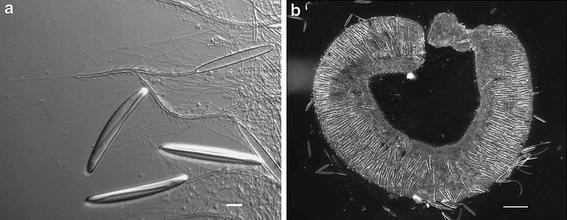
Mechanism of Nematocyst Discharge and Its Cellular Control Cnidarians possess unique intracellular organelles, cnidae, which discharge by evaginating their tubular contents following certain appropriate stimuli. Every cnida consists of a capsule, a tubule or shaft, or combination of the two, and intracapsular fluid and is contained in a cell called a cnidocyte.
Nematocysts – The Stinging Cells | Zoology for IAS, IFoS and... The discharged nematoblasts are replaced by the new one. Nematocysts do not require nervous stimuli for activation, although in fully fed animals, nematocysts are not discharged when they come in contact with food. TYPES OF NEMATOCYSTS About 30 different types of nematocysts are found in different groups of cnidarians.
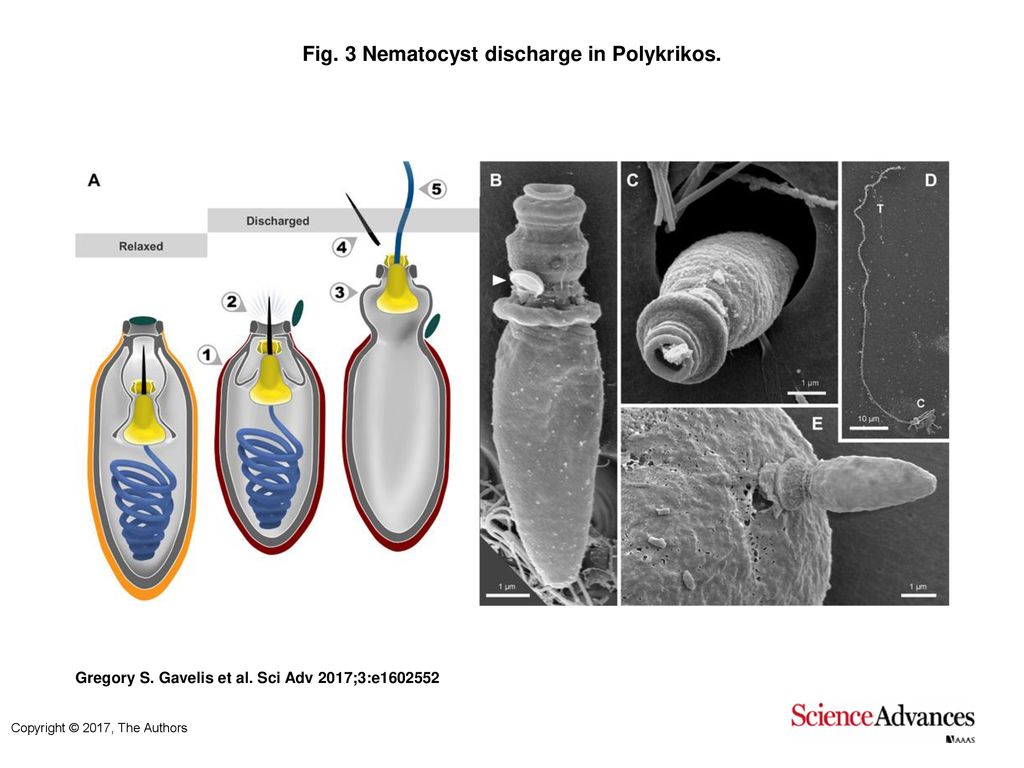
What Causes A Nematocyst To Discharge? - WWFAQs - World Wide FAQs How the nematocysts are discharged out of the cnidocytes? When the trigger is activated, the tubule shaft of the cnidocyst is ejected and, in the case of the penetrant nematocyst, the forcefully ejected tubule penetrates the target organism. This discharge takes a few microseconds, and is able to reach accelerations of about 40,000 g.
When do nematocysts discharge? - odne.bluejeanblues.net What triggers the nematocysts on a Hydra? When the animal is feeding or is alarmed, the cnidocytes are triggered to release the nematocysts. When the animals is feeding, most of the nematocysts that are released are hollow and elongate, their purpose being to trap and entangle prey. How does a nematocyst work how quick does it discharge?
What causes a nematocyst to discharge? - Answers Nematocyst discharge is triggered by an immediate approach or a foreign stimulus. When the cell is discharged, a brand new nematocyst is created as the system in each cell can only be activated...
An in-vitro examination of the effect of vinegar on discharged ... - PubMed Objective: To determine the effect acetic acid (vinegar) has on discharged nematocysts in a simulated sting from Chironex fleckeri. Method: This research was performed in 2 parts: 1 C. fleckeri tentacles placed on amniotic membrane were electrically stimulated, and venom washings collected before and after application of vinegar. . Lyophilised venom washings were run through a fast-performance ...
Force-dependent discharge of nematocysts in the sea anemone Summary. Sea anemones discharge cnidae ('stinging capsules' including nematocysts) to capture prey and to defend themselves. In the present study, we tested the relationship between the force of test probes striking feeding tentacles and discharge of microbasic p-mastigophore nematocysts into the test probes. In seawater alone, the response curve is bimodal with maximal discharge observed ...
Corals Tutorial: Nematocyst Cell - National Ocean Service The diagram above shows the anatomy of a nematocyst cell and its “firing” sequence, from left to right. On the far left is a nematocyst inside its cellular capsule. The cell’s thread is coiled under pressure and wrapped around a stinging barb. When potential prey makes contact with the tentacles of a polyp, the nematocyst cell is stimulated.
Nematocyst | biology | Britannica The stinging effect of nematocysts in the Portuguese man-of-war and some jellyfish ( qq.v.) species can be extremely painful to humans and may cause paralysis, shock, and even death. More From Britannica cnidarian Nematocysts are a type of cnidae, and it is the presence of cnidae that separates jellyfish and other cnidarians from other animals.
Nematocyst - Structure, Function, Types and FAQs - VEDANTU Jan 22, 2023 · Types of Nematocysts: Meaning of nematocysts have over 30 different forms of cnidae. They are classified into the following categories: Penetrant: The penetrant, also known as the stenotele, is the biggest and therefore most complex of the nematocysts. Once it is released, it penetrates the prey's surface or chitinous exoskeleton and inserts a venomous fluid called hypnotoxin, which either paralyses or destroys the victim.
Nematocyst Discharge Smithsonian Magazine Nematocyst Discharge. This cell is one of thousands on the tentacles of this starlet sea anemone and other cnidarians, including hydra and jellyfish. These cells contain poison darts that sting ...
Cnidocyte - Wikipedia When discharged, it pierces the skin or chitinous exoskeleton of the prey and injects the venomous fluid, hypnotoxin, that either paralyzes the victim or kills it. Glutinant: a sticky surface used to stick to prey, referred to as ptychocysts and found on burrowing (tube) anemones, which help create the tube in which the animal lives
Nematocyst Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster ni-ˈma-tə-. : one of the stinging capsular organelles of the tentacle of a cnidarian (such as a box jellyfish or sea anemone) that contains a coiled, hollow, usually barbed, venomous thread which is discharged especially for catching prey and defending against enemies. Each nematocyst contains a spiral-coiled thread tipped with a toxin-bearing barb that can be ejected into the skin.
The Cell Biology of Nematocysts - ScienceDirect The ability of epidermal stenotele nematocysts to discharge suggest that this hydra organelle preserved its physiological properties in the new host. Research article. Nematocyst types and venom effects of Aurelia aurita and Velella velella from the Mediterranean Sea. Toxicon, Volume 175, 2020, pp. 57-63.
Cnidaria Toxicity - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Nematocysts are hollow, barbed tubes that inject venom into the victim's skin at a force of two to five pounds per square inch (13-34 kPa). The nematocysts are located along the jellyfish's tentacles and discharge using a "spring mechanism" upon contact with the prey.[1] The stinging mechanism can still function even if the organism is dead.
Nanosecond-scale kinetics of nematocyst discharge - Current Biology The rapid discharge of stinging cells (nematocytes) in jellyfish, hydra, and other cnidarians is one of the fastest movements in the animal kingdom. After the triggering of exocytosis, a miniature cellular weapon, the nematocyst, is released and stylets punch a hole into the prey's integument. This step is so fast that conventional high-speed micro-cinematography fails to resolve its kinetics [1].

























Post a Comment for "42 nematocysts discharge when"